Cancer Res.:癌干细胞疫苗具有抗肿瘤疗效
2012-04-14 towersimper 生物谷
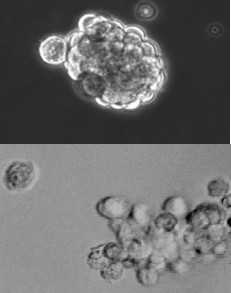
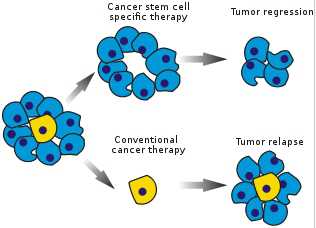
癌干细胞(cancer stem cell)是一类能够抵抗化疗或者放疗的肿瘤细胞,能够让肿瘤再生从而导致肿瘤复发。尽管名字存在类似性,但是癌干细胞与胚胎干细胞存在很大的差别。 美国密歇根大学外科研究助理教授Qiao Li博士和同事们从两类具有免疫活性的小鼠模式动物中提取癌干细胞,然后利用它们制备疫苗。 “我们发现这些富集的癌干细胞具有免疫原性,相比于在以前的免疫治疗试验中通常使用不加选择的肿瘤

癌干细胞(cancer stem cell)是一类能够抵抗化疗或者放疗的肿瘤细胞,能够让肿瘤再生从而导致肿瘤复发。尽管名字存在类似性,但是癌干细胞与胚胎干细胞存在很大的差别。
美国密歇根大学外科研究助理教授Qiao Li博士和同事们从两类具有免疫活性的小鼠模式动物中提取癌干细胞,然后利用它们制备疫苗。
“我们发现这些富集的癌干细胞具有免疫原性,相比于在以前的免疫治疗试验中通常使用不加选择的肿瘤细胞作为抗原来源,把它们作为抗原效果更加显著”,Li说,“对这种现象的内在机制研究表明当用癌干细胞进行免疫产生抗体后,这些抗体能够靶向癌干细胞,从而产生抗肿瘤免疫。”
研究人员也发现从接受癌干细胞疫苗注射的小鼠中收集的杀伤性T淋巴细胞能够在体外杀死癌干细胞。
这项研究是免疫治疗研究领域的一项比较大的突破,因为研究人员能够使用纯化的癌干细胞来制备疫苗,而且这种癌干细胞疫苗能够强化抗体和T细胞选择性靶向癌干细胞的能力。
相关研究结果于2012年4月1日发表在Cancer Research期刊上
原始链接:http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=22473314

Cancer Stem Cell Vaccination Confers Significant Antitumor Immunity
Ning Ning, Qin Pan, Fang Zheng, Seagal Teitz-Tennenbaum, Martin Egenti, Ji Yet, Mu Li, Christophe Ginestier, Max S. Wicha, Jeffrey S. Moyer, Mark E.P. Prince, Yingxin Xu, Xiao-Lian Zhang, Shiang Huang, Alfred E. Chang, and Qiao Li
Most studies of cancer stem cells (CSC) involve the inoculation of cells from human tumors into immunosuppressed mice, preventing an assessment on the immunologic interactions and effects of CSCs. In this study, we examined the vaccination effects produced by CSC-enriched populations from histologically distinct murine tumors after their inoculation into different syngeneic immunocompetent hosts. Enriched CSCs were immunogenic and more effective as an antigen source than unselected tumor cells in inducing protective antitumor immunity. Immune sera from CSC-vaccinated hosts contained high levels of IgG which bound to CSCs, resulting in CSC lysis in the presence of complement. CTLs generated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells or splenocytes harvested from CSC-vaccinated hosts were capable of killing CSCs in vitro. Mechanistic investigations established that CSC-primed antibodies and T cells were capable of selective targeting CSCs and conferring antitumor immunity. Together, these proof-of-concept results provide a rationale for a new type of cancer immunotherapy based on the development of CSC vaccines that can specifically target CSCs.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#Res.:#
23
#癌干细胞#
25